Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Bruising
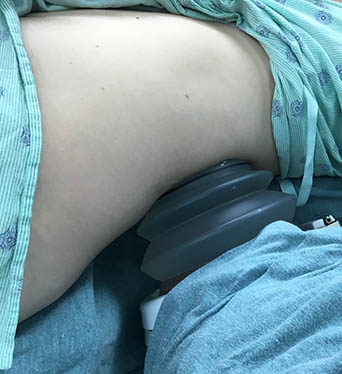
Skin bruising at shock wave entry site.
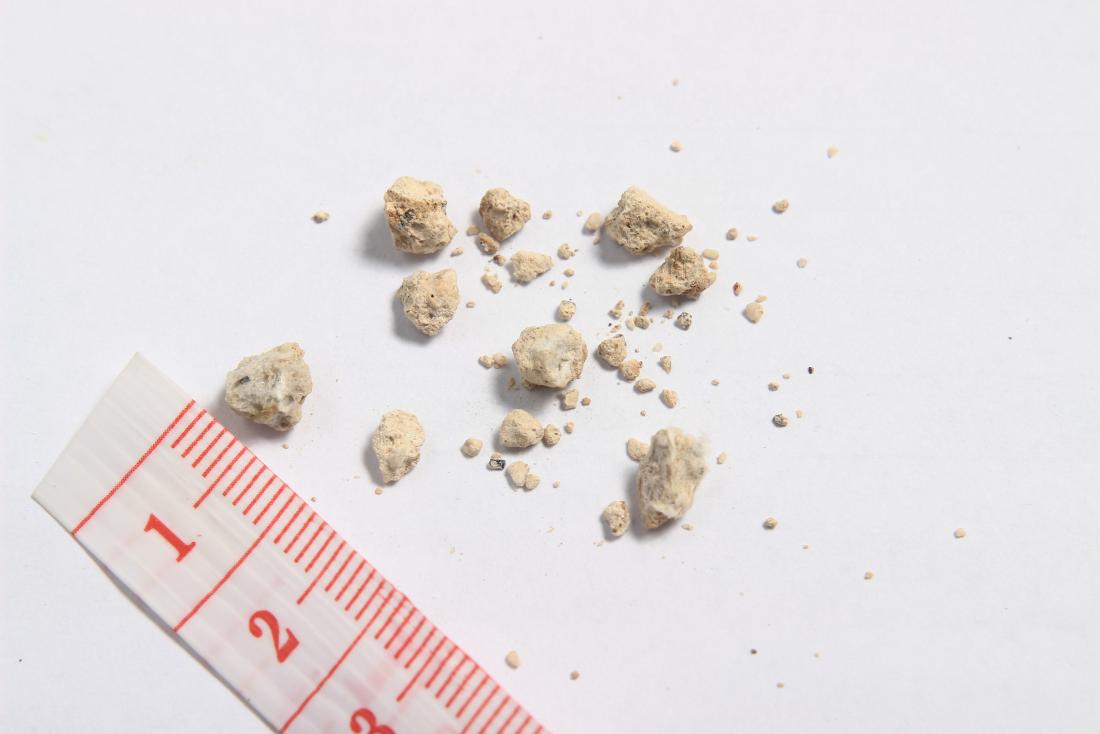
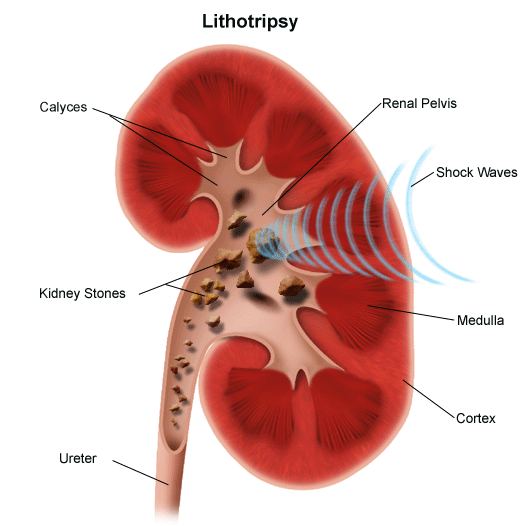
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy bruising. A review of the literature since its inception journal of the american college of surgeons 10 1016 j jamcollsurg 2003 06 006 198 1 128 135 2004. Once the stones are broken up they can travel down the ureter the tube leading from the kidney to the bladder and into the bladder more easily. More serious problems are less likely but can include. Patients who once required major surgery to remove their stones could be treated with eswl and not even require an incision.
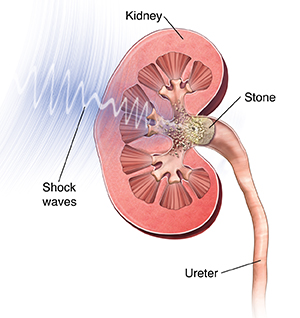
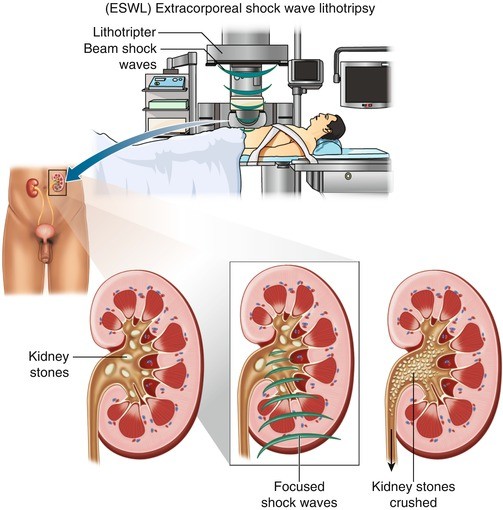
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy eswl is a type of treatment for kidney stones. Occurs in 1 7 of patients following extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy as a result of the release of bacteria from the fragmentation of infected. Shock wave lithotripsy for kidney stones can cause side effects such as cramps or blood in your urine. Your kidney stones have been treated with eswl extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy.
Due to the need to target the stone eswl is usually reserved for patients with. Serious complications including life threatening bleeding injury to surrounding structures and death are extremely rare. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy eswl is a noninvasive means of treating kidney and upper ureteral stones. Complications are infrequent with the most common being bleeding infection and distal ureteral obstruction by fragments.
Abstract extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is an attractive and well tolerated option for treatment of renal and ureteral calculi. After the procedure the kidney stones should be small enough to pass out of your body in your urine. That means breaks the stones without placing any instruments inside the body. As such eswl is the.
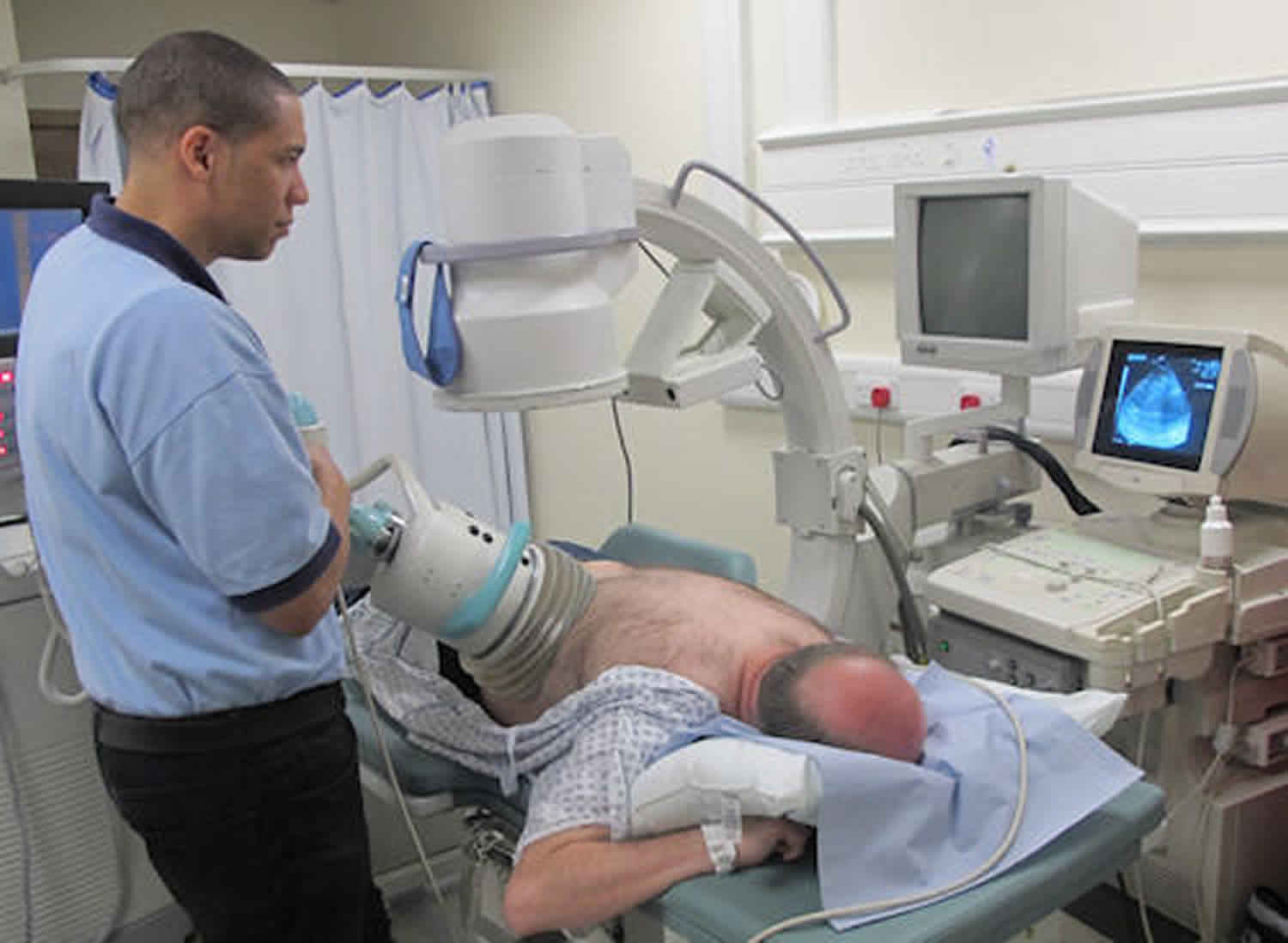
Lithotripsy is a procedure that uses shock waves or lasers to break down stones in the kidneys bladder or ureter. The introduction of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy eswl in the early 1980s revolutionized the treatment of patients with kidney stone disease. The procedure uses sound shockwaves through the flank under x ray guidance to fragment the stone and then relies on spontaneous passage of the fragments. In this article learn about how the procedure works the success rate how to.
Click on the article title to read more.