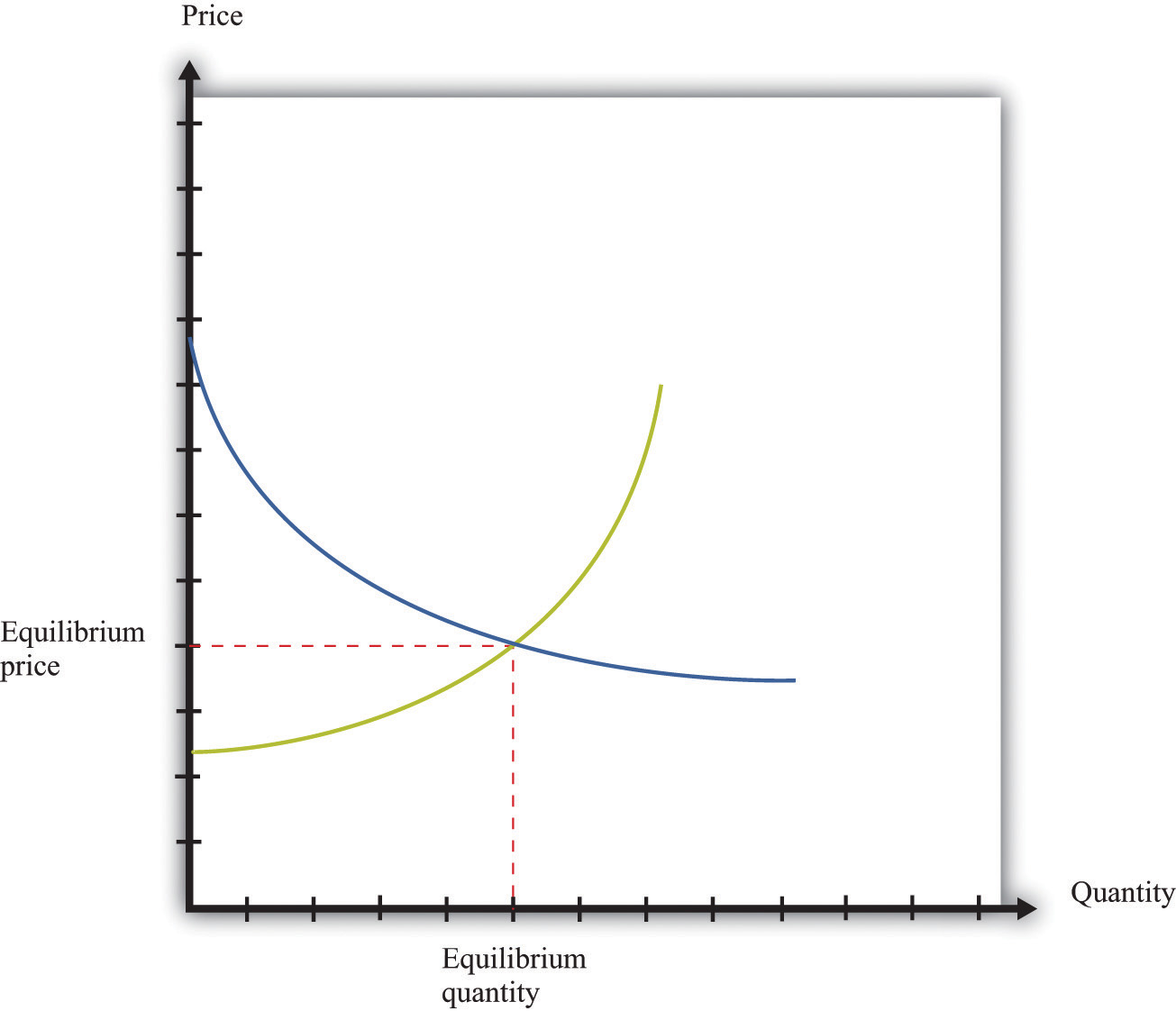
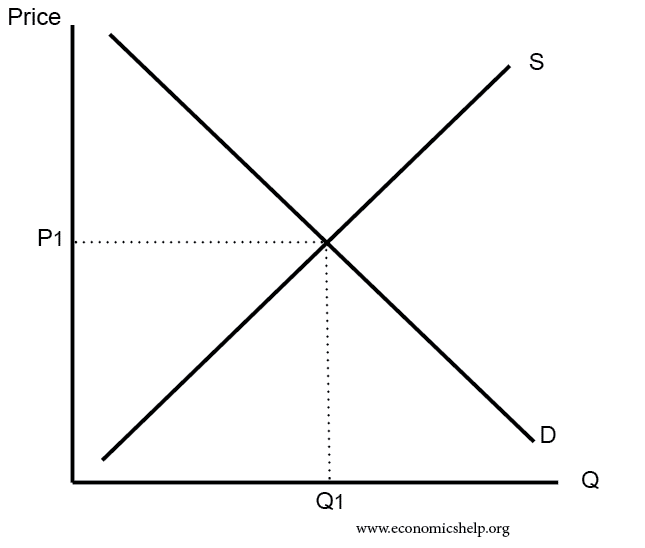
Supply And Demand Graph With Equilibrium Price Displayed
/EquilibriumQuantity-3d51042295814ceda425f70c182d9e76.png)
4 25 b the supply curve has been assumed to be perfectly elastic.
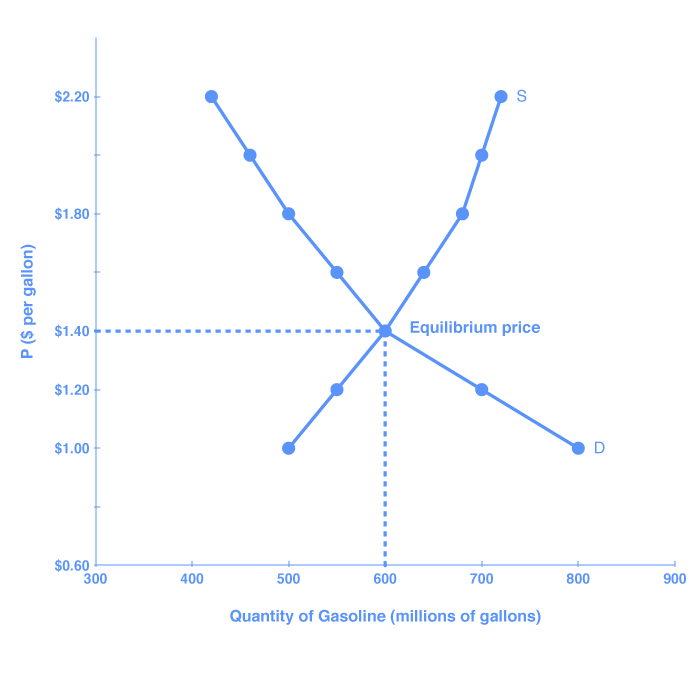
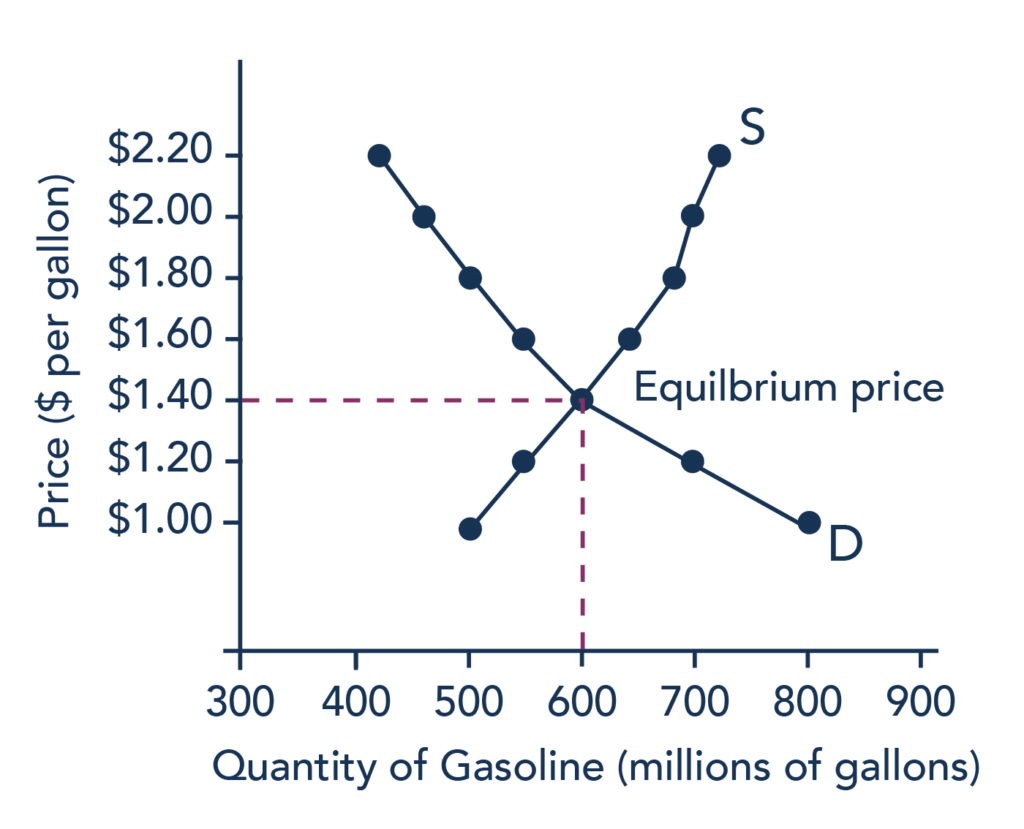
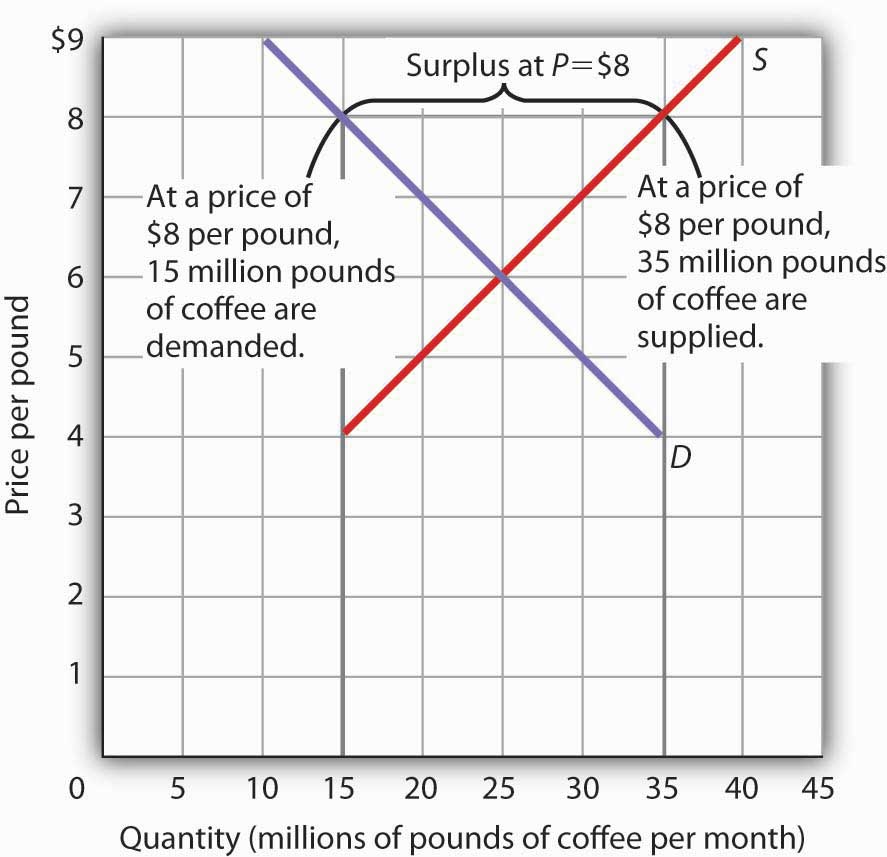
Supply and demand graph with equilibrium price displayed. An individual demand curve shows the quantity of the good a consumer would buy at different prices. In this example the lines from the supply curve and the demand curve indicate that the equilibrium price for 50 inch hdtvs is 500. Demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve d and the supply curve s intersect at the equilibrium point e with a price of 1 40 and a quantity of 600. The market for coffee is in equilibrium.
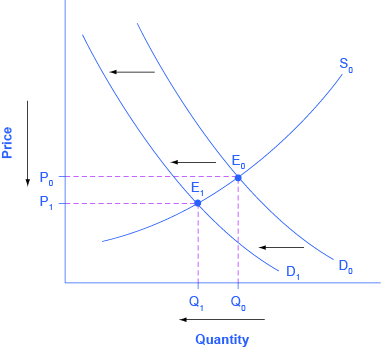
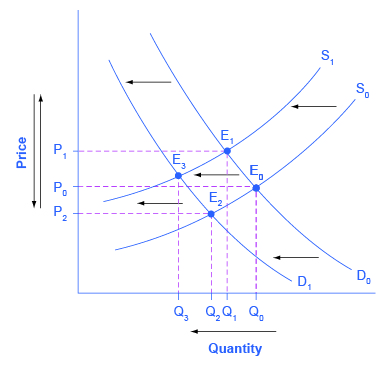
Unless the demand or supply curve shifts there will be no tendency for price to change. Plotting price and quantity supply market equilibrium more demand curves. The demand curve d and the supply curve s intersect at the equilibrium point e with a price of 1 40 and a quantity of 600. B calculate the ped at the point of equilibrium.
Demand and supply for gasoline. The example supply and demand equilibrium graph below identifies the price point where product supply at a price consumers are willing to pay are equal keeping supply and demand steady. A is the intercept of the demand and supply curves. Supply formula qs a bp.
B is the slope of two curves. Let the demand curve and supply curve be represented by q 5p 30 and q 2p 20 respectively. By substituting demand and supply formula to the given example equilibrium quantity and price can be calculated. In other words it is the demand and supply quantities at price zero.
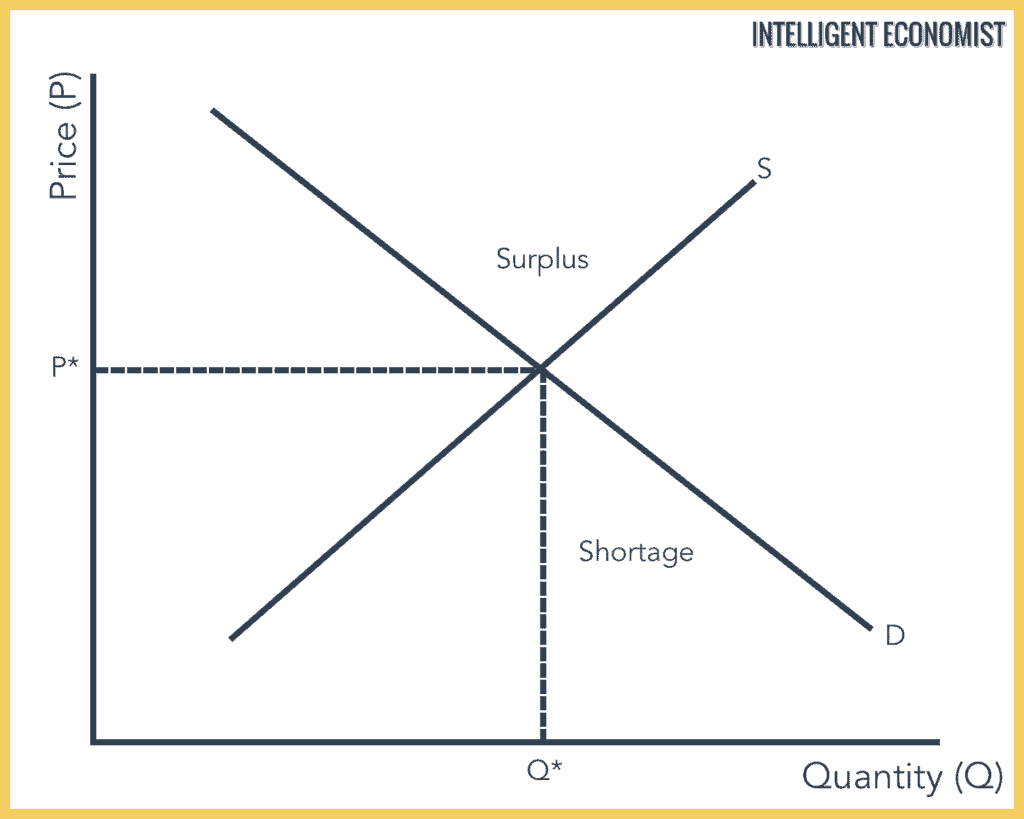
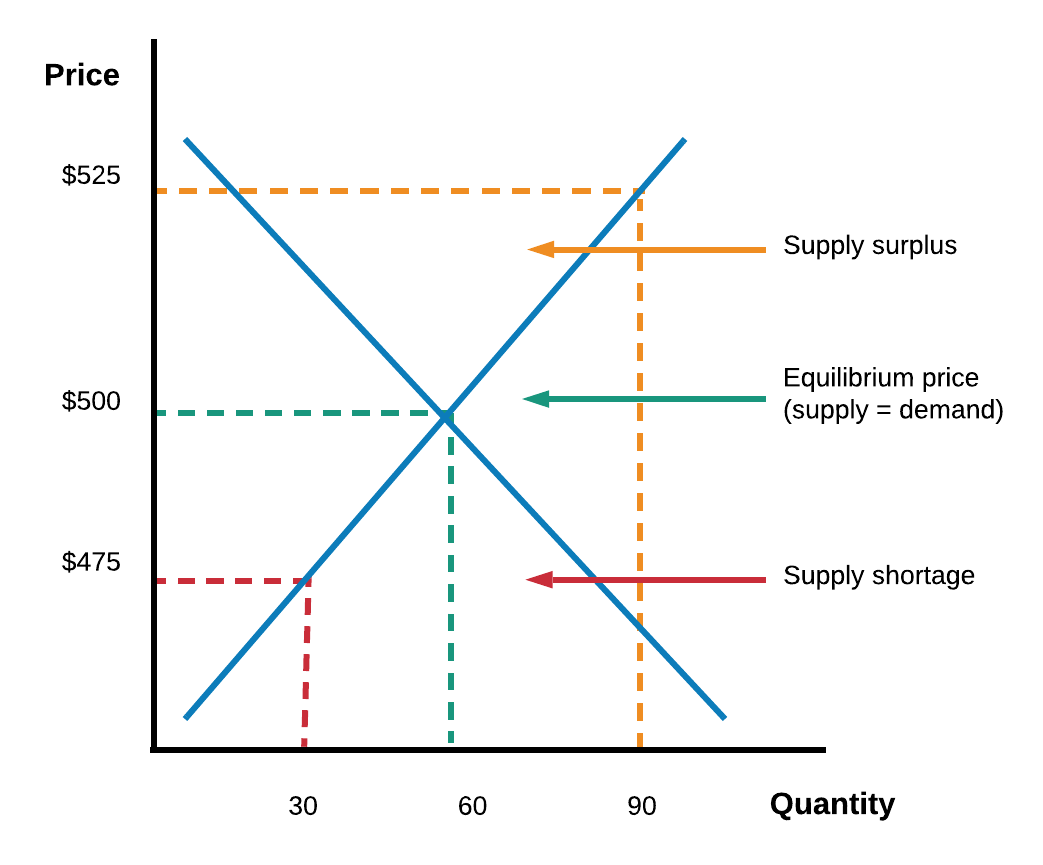
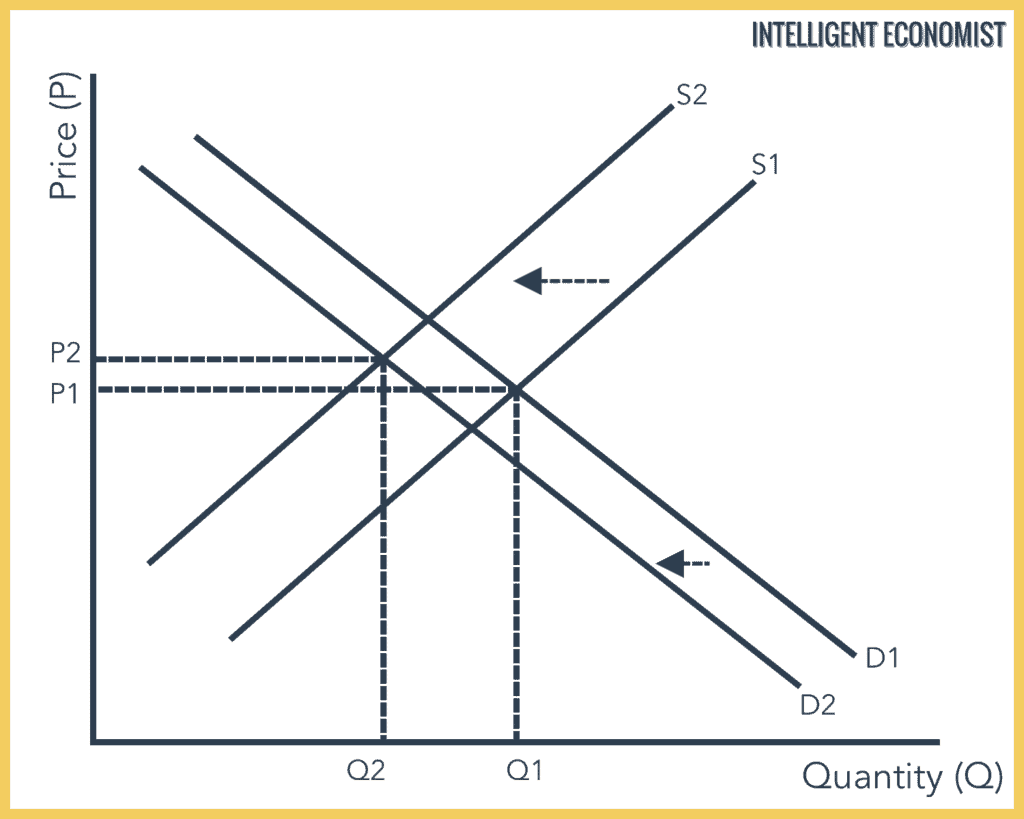
Demand formula qd a bp. The equilibrium is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. The equilibrium price in any market is the price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The supply and demand graph can be used to visually see how a change in demand and or supply changes quantity bought and sold in a market and the market price.
A calculate the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. This can be calculated by. The demand curve shows the amount of goods consumers are willing to buy at each market price. You can see visually that the market clearing number of rides is close to 23 000 at a price of 2 7 per km.
The equilibrium is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied.