Supply And Demand Graph With Excise Tax
Taxes are among the market and regulatory conditions that define the demand curve.
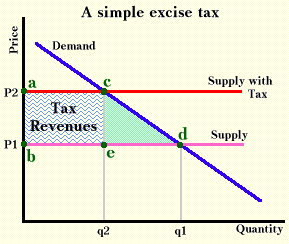
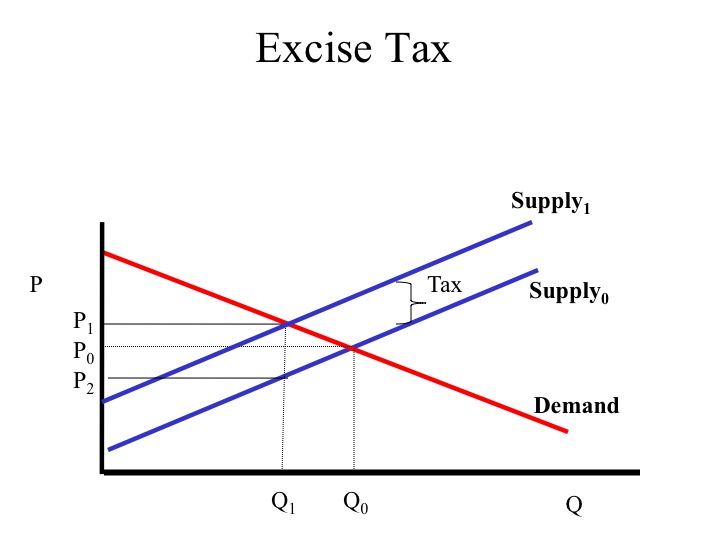
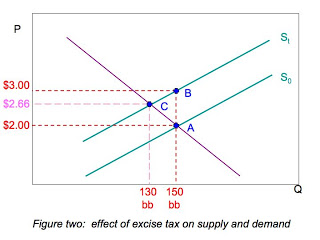
Supply and demand graph with excise tax. This demonstration shows the effect of an excise tax on a perfectly competitive market. It is illustrated as the supply curve shifts from s 0 to s 1. While demand for the product has not changed all of the determinants of demand are the same consumers are required to pay a higher price which is why we see the new equilibrium point occurring at a higher price and lower quantity. Quantity shifts from q 0 to q 1 after the excise tax is imposed on the production of good a.
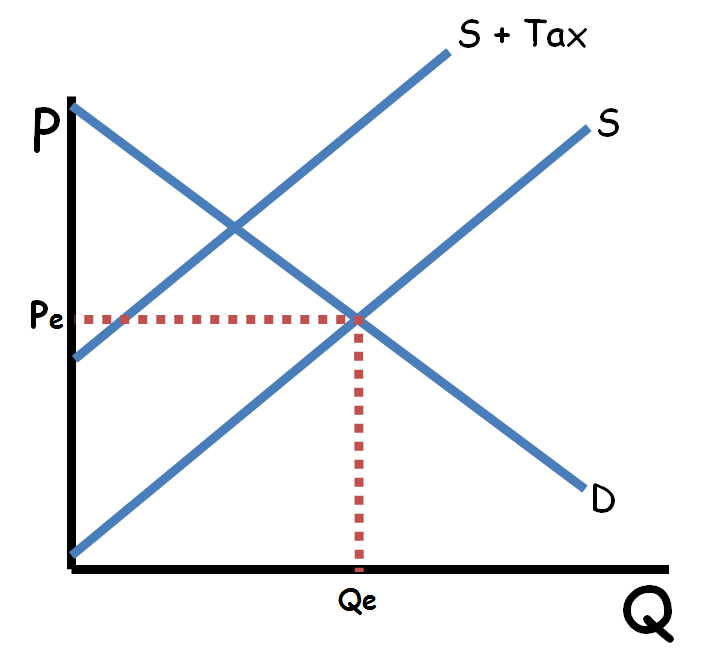
Excise tax imposed on producers. Ap is owned by the college board which does not endorse this site or the above review. It is also the amount the demand curve shifts from d 0 to d 1. Consider the supply and demand diagram below.
1 show supply demand with an equilibrium price a. Refer to the supply and demand diagram below. A tax on buyers is thought to shift the demand curve to the left reduce consumer demand because the price of goods relative to their value to consumers has gone up. Additionally the demonstration shows and calculates the revenue for the government raised by the tax.
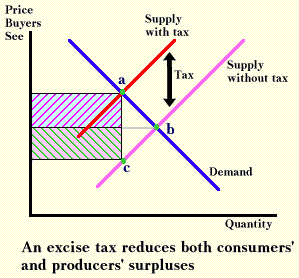
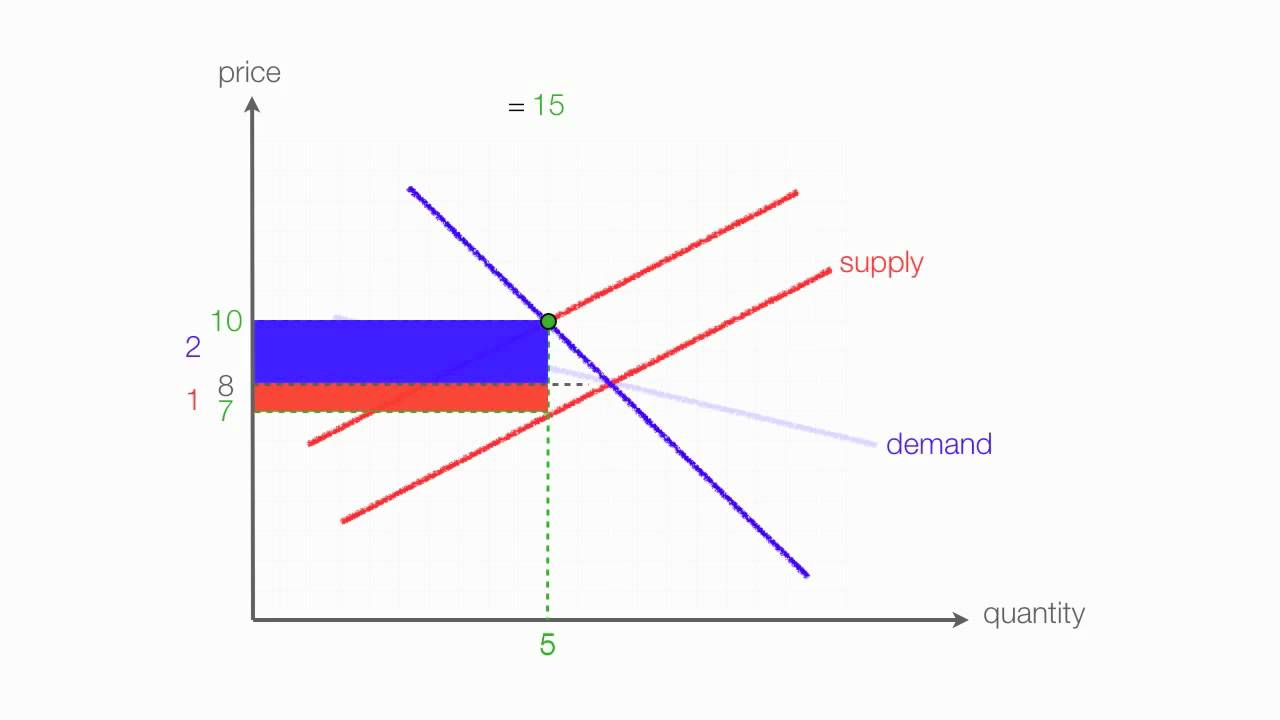
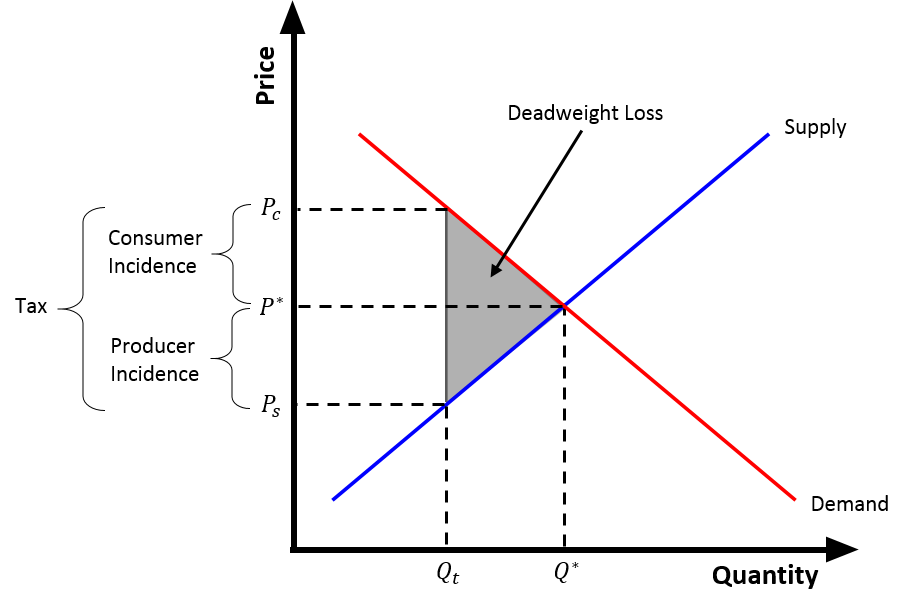
As stated by wecon the demand curve will shift down. When the tax is introduced the consumer surplus orange and producer surplus blue shrink while deadweight loss purple the inefficiency caused by the tax increases. To answer the later problem we need to look at price elasticity of supply and of demand. The sales tax on the consumer shifts the demand curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in demand for the product because of the higher price.
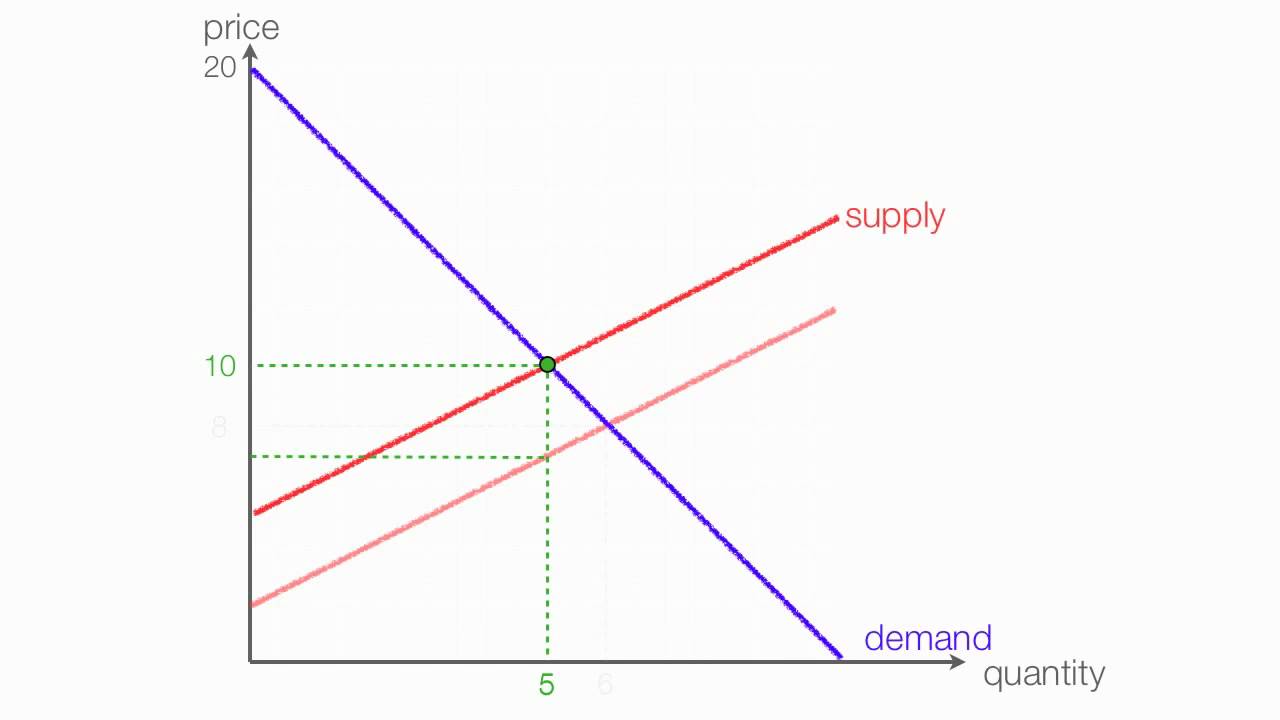
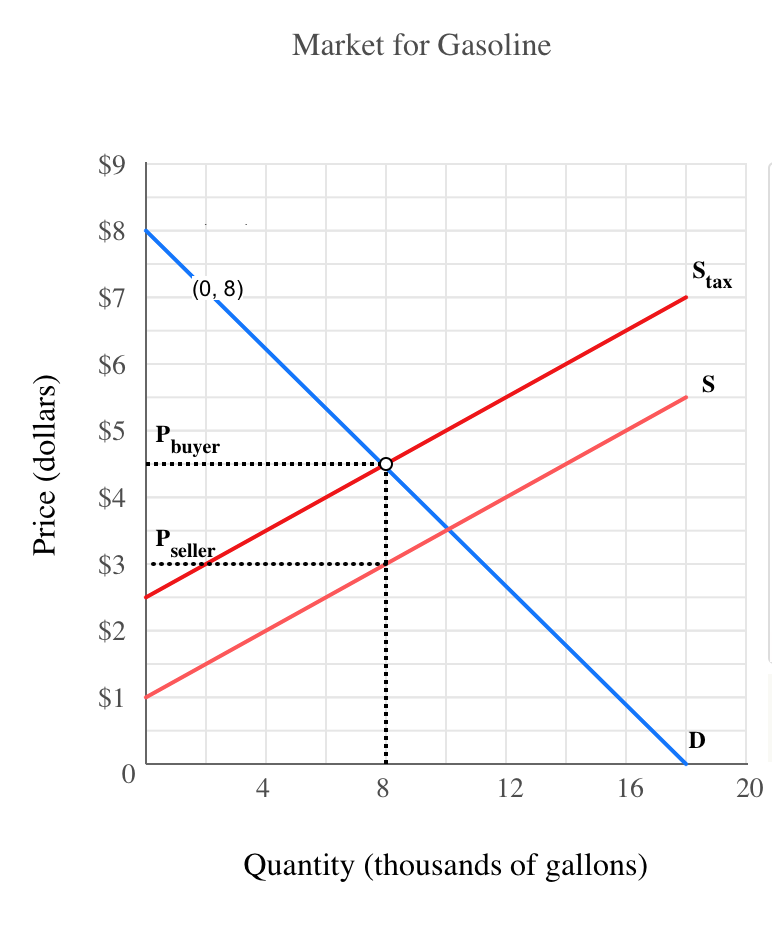
When a government imposes an excise tax on a good however it drives a wedge between the supply curve and the demand curve forcing a new equilibrium where the amount paid by the consumer is. It is two different things to determine which curve will shift and who will actually bear the burden of the tax. If an output excise tax of 5 per unit is introduced in this market the price that consumers pay will equal and the price that producers receive net of the tax will equal. If the graph shows quantities demanded and quantities supplied as a function of the price received by producers the supply curve would stay fixed and the demand curve would shift vertically downward by the amount of the tax.