Supply And Demand Graph If Demand Increases
The concept of demand can be defined as the number of products or services is desired by buyers in the market.
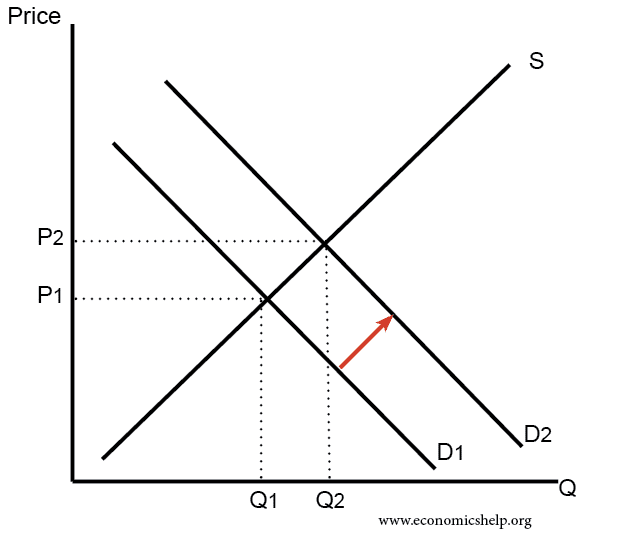
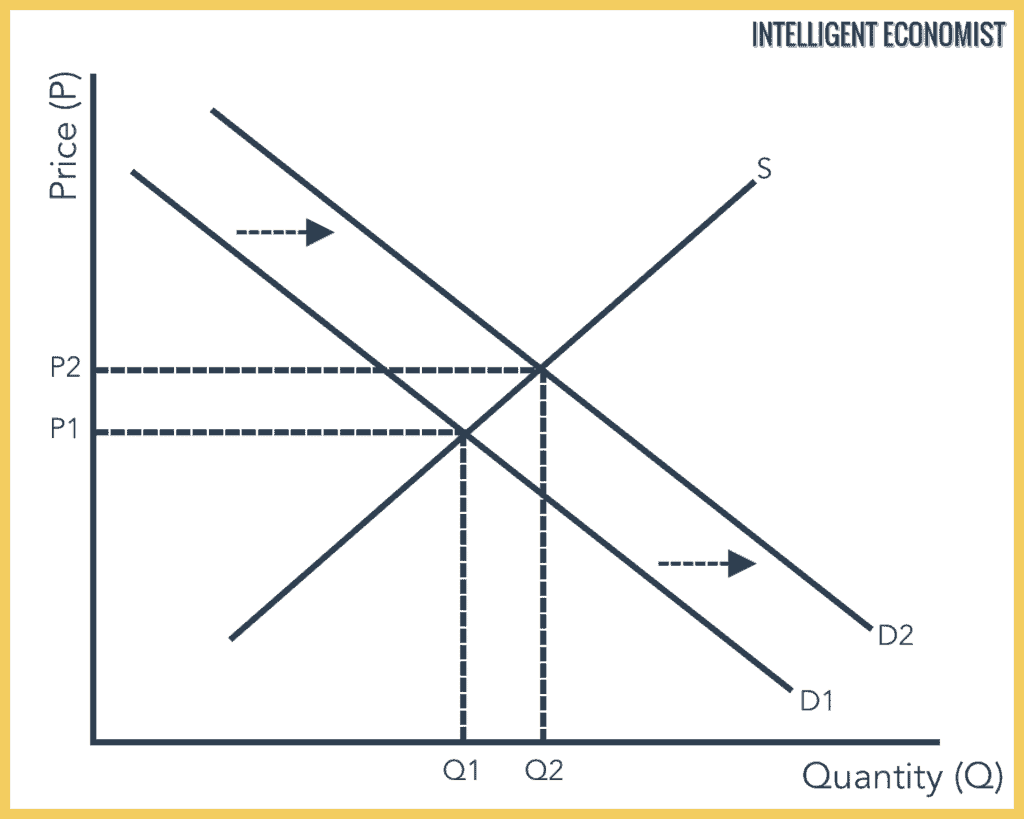
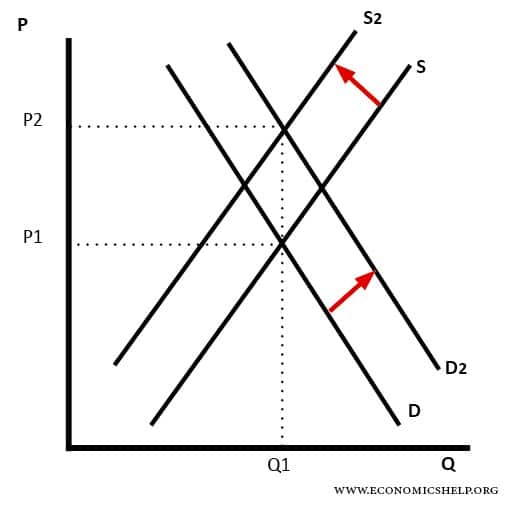
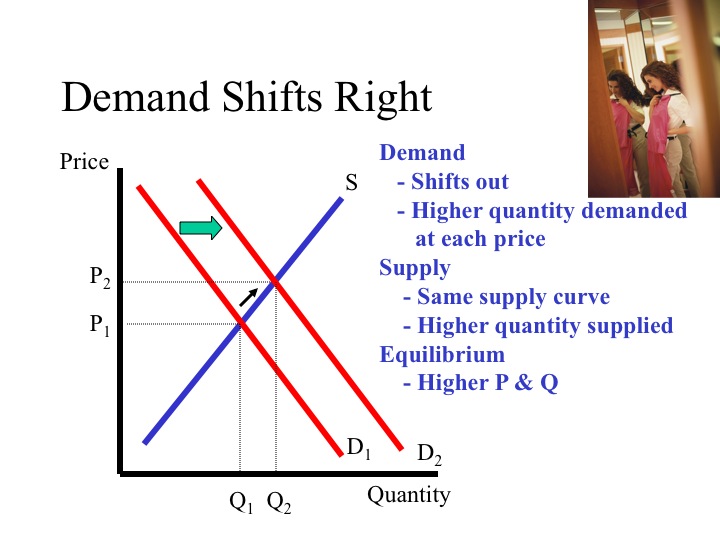
Supply and demand graph if demand increases. Increase in demand illustration of an increase in equilibrium price p and equilibrium quantity q due to a shift in demand d. When there is an increase in demand with no change in supply the demand curve tends to shift rightwards. Supply and demand are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy. If demand increases and supply remains unchanged then it leads to higher equilibrium price and quantity.
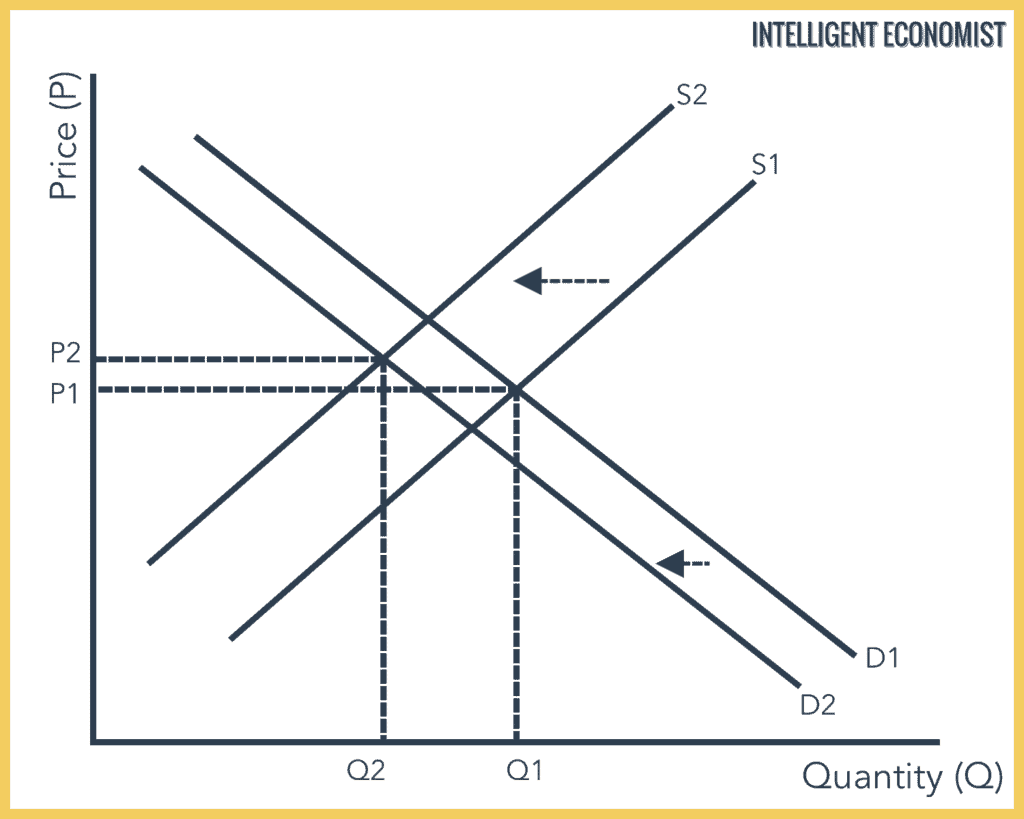
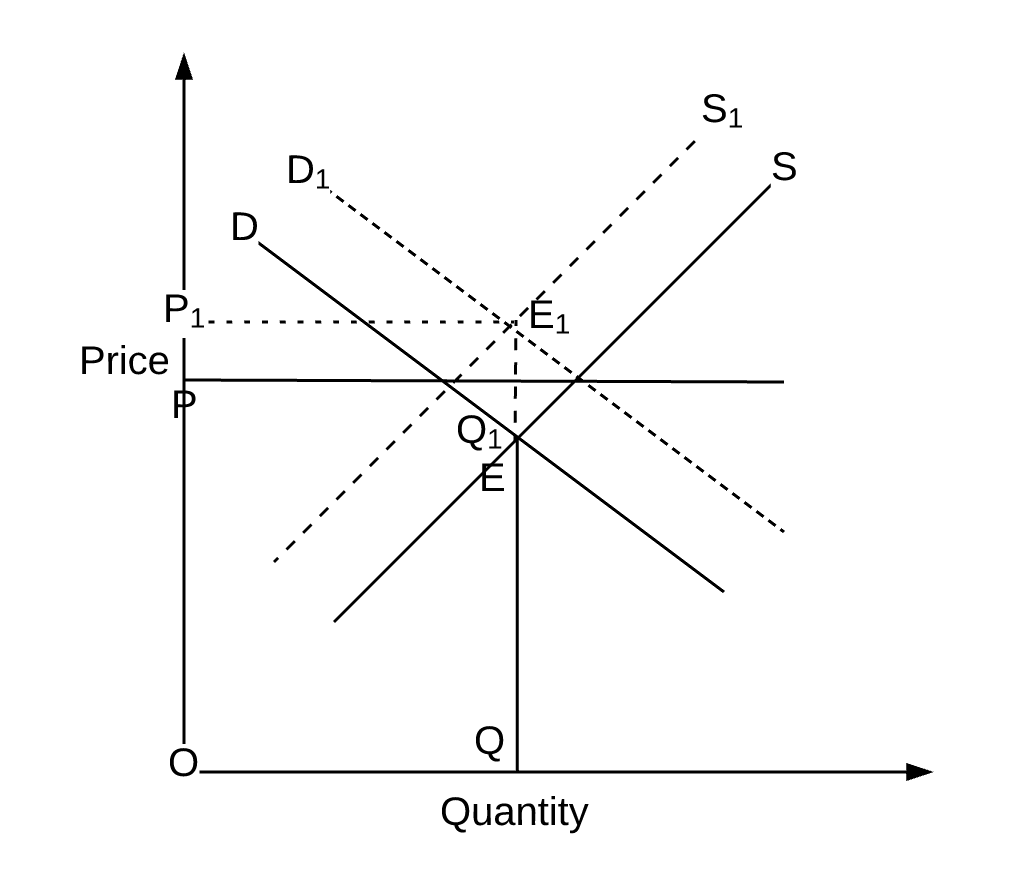
It leads to a leftward shift in the demand curve of inferior good from dd to d 1 d 1. An increase or decrease in income affects the demand inversely if the given commodity is an inferior good. Because this is greater than the quantity producers are providing still q 0 as determined off the supply curve a shortage exists. Similarly when demand curve shifts downward to d 2 d 2 price and quantity decline to op 2 and oq 2 respectively.
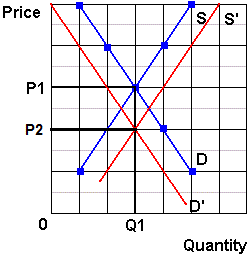
The four basic laws of supply and demand are. The main demand and supply shifts from market equilibrium. Through the demand curve the relationship between price and quantity demanded is clearly illustrated. At any given point in time the supply of a good brought to market is fixed.
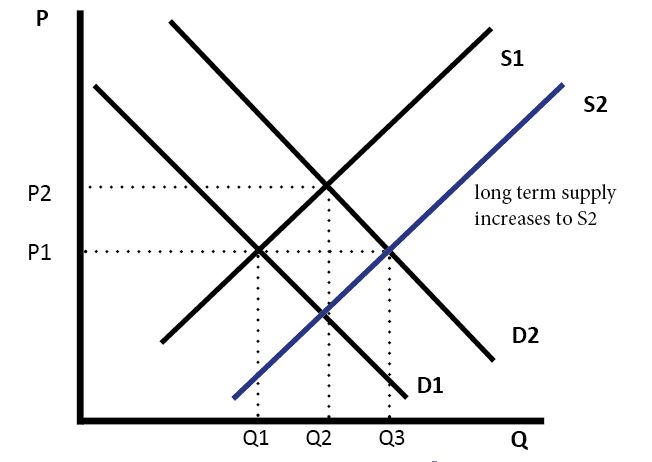
Intuitively if the price for a good or service is lower there is a higher demand for it. From the demand schedule above the graph can be created. Increase demand increase supply decrease in demand decrease in supply. If demand increases demand curve will shift to d 1 d 1 and the new equilibrium price will rise to op 1 and quantity demanded and supplied will increase to oq 1.
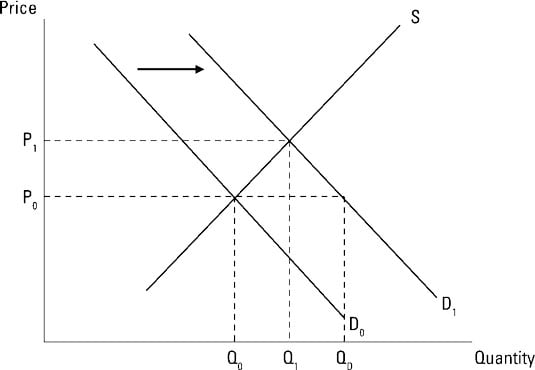
4 25 b the supply curve has been assumed to be perfectly elastic. The quantity demanded associated with the price p 0 is now q d. In other words the supply curve in this case is a vertical line while the demand curve is always downward sloping due. If demand increases the demand curve shifts to the right from d 0 to d 1.
Originally the market was in equilibrium at price p 0 and quantity q 0. Any change in non price factors would cause a shift in the demand curve whereas changes in the price of the commodity can be traced along a fixed demand curve. As income increases the demand for inferior goods say black and white tv falls from oq to oq 1 at the same price of op. As the price for notebooks decreases the demand for notebooks increases.
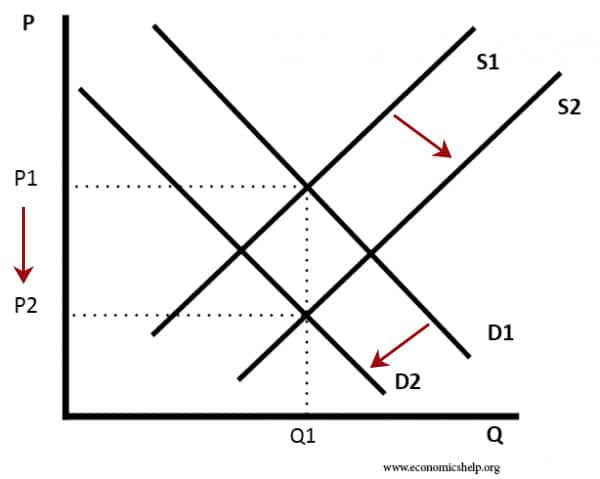
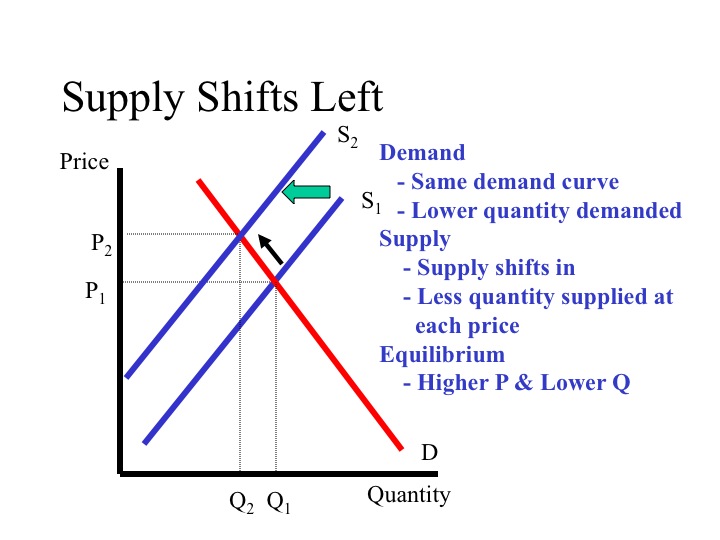
As the demand increases a condition of excess demand occurs at the old equilibrium price. If demand decreases and supply remains unchanged then it leads to lower equilibrium price and quantity. Note that in this case there is a shift in the demand curve. A change in demand can be recorded as either an increase or a decrease.