Supply And Demand Graphs Increase In Demand
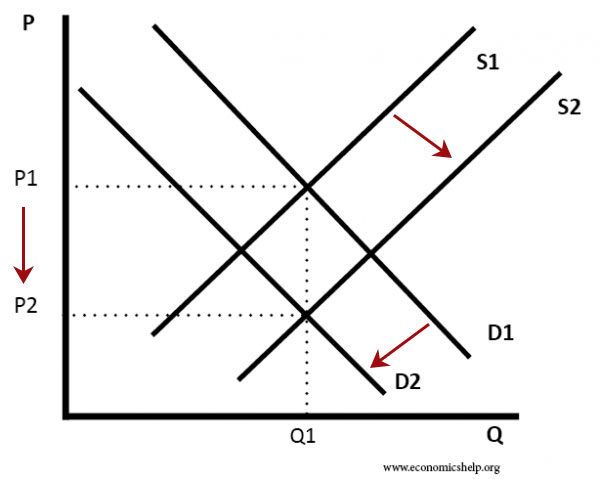
Increase in demand decrease in supply.
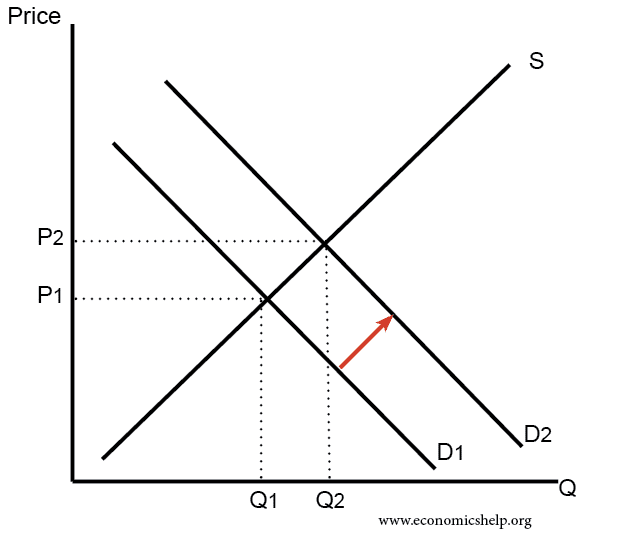
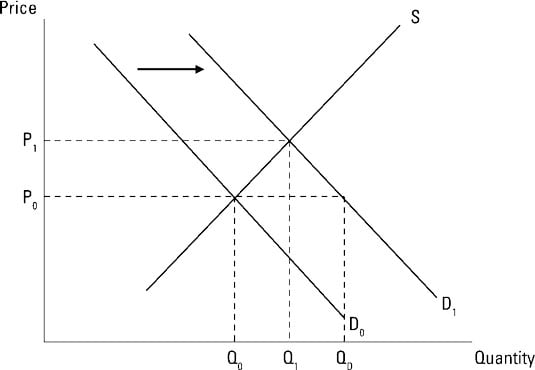
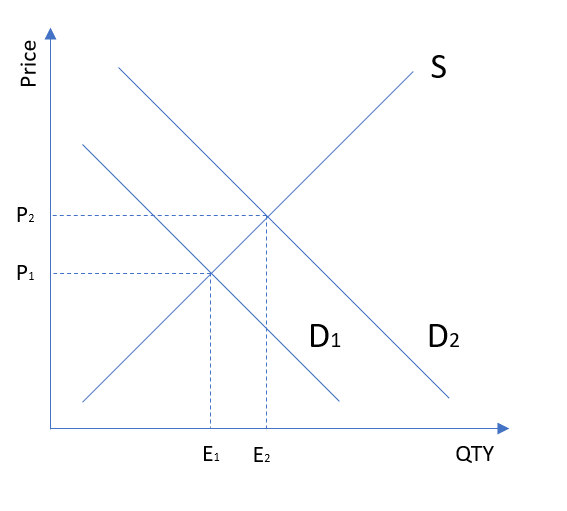
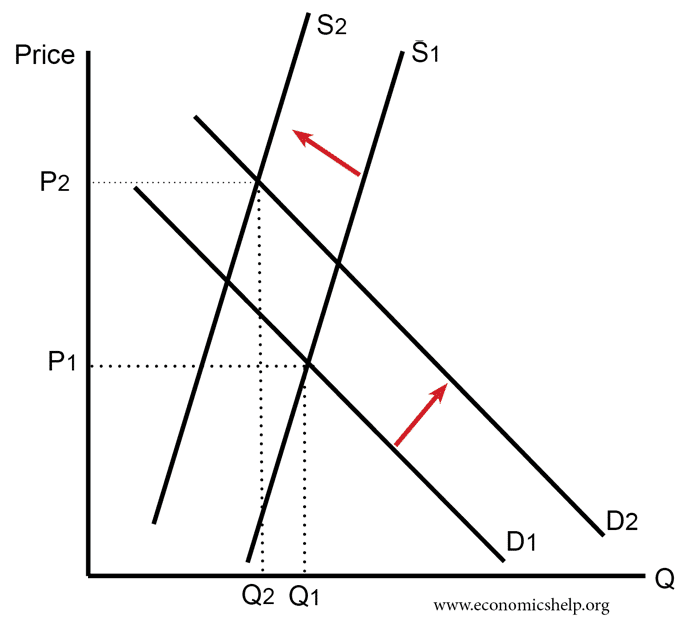
Supply and demand graphs increase in demand. In this diagram supply and demand have shifted to the right. If prices did not adjust this balance could not be maintained. A rightward shift refers to an increase in demand or supply. Demand curves are used to determine the relationship between price and quantity and follow the law of demand which states that the quantity demanded will decrease as the price increases.
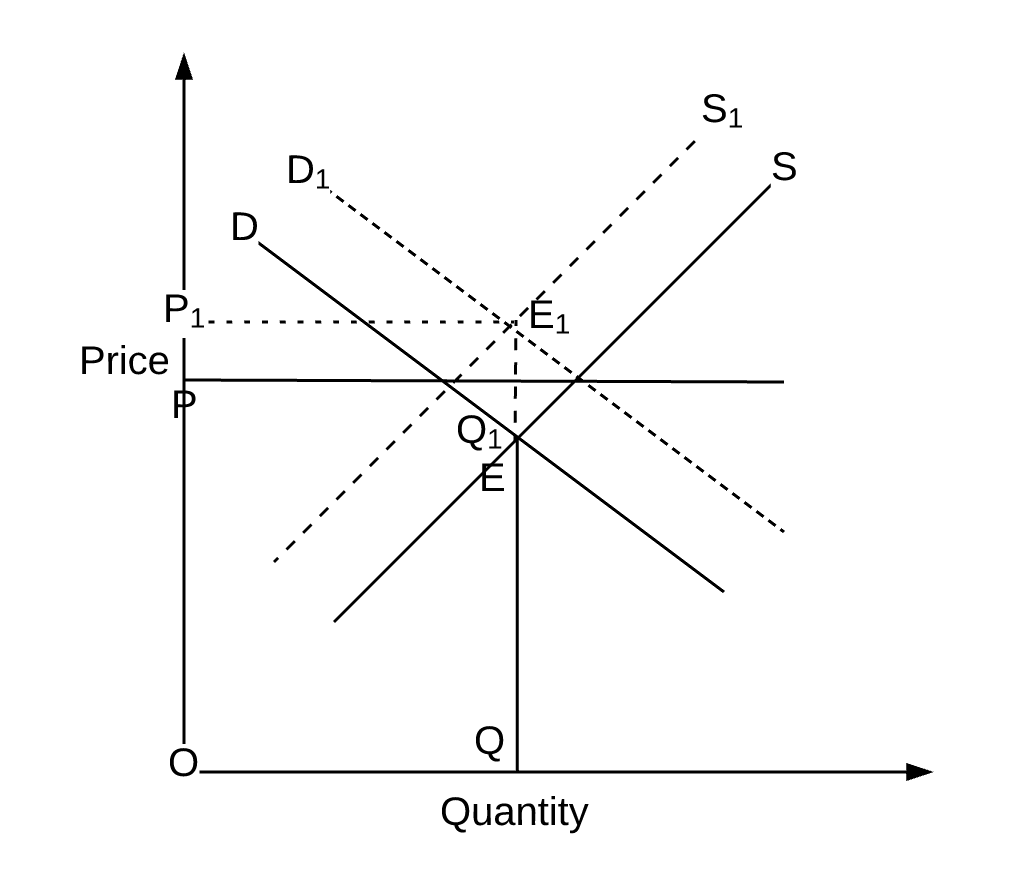
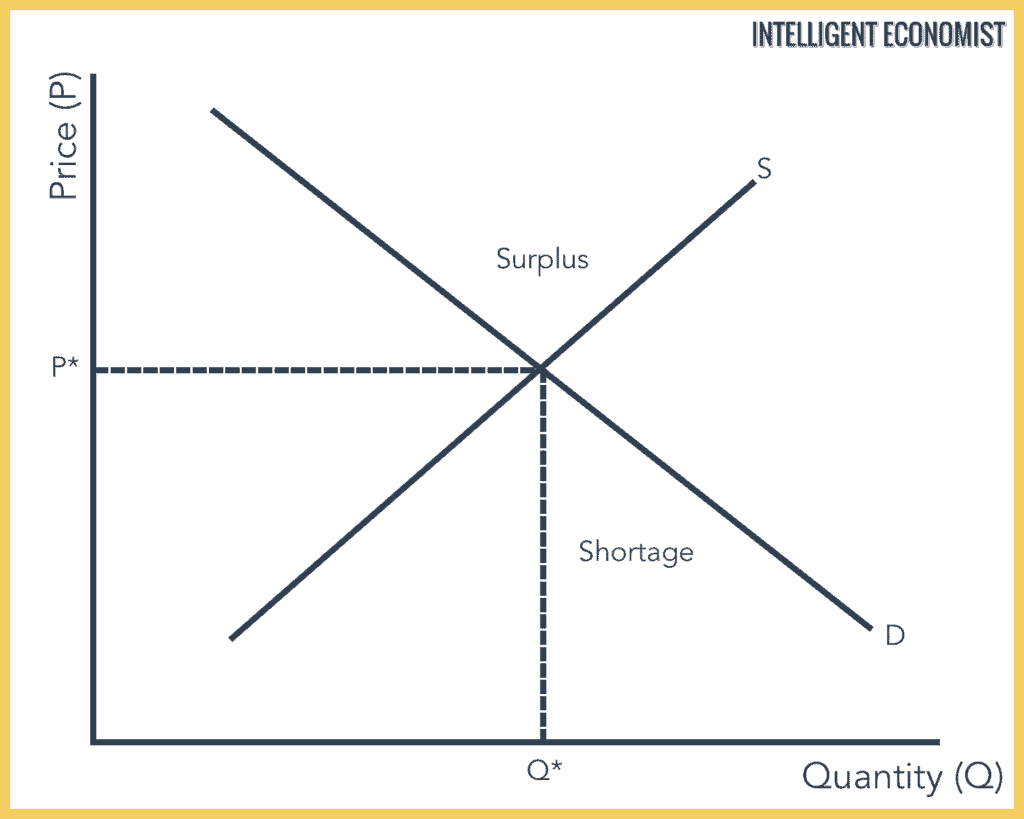
The concept of demand can be defined as the number of products or services is desired by buyers in the market. As demand and supply curves shift prices adjust to maintain a balance between the quantity of a good demanded and the quantity supplied. The main demand and supply shifts from market equilibrium. Notice that the demand and supply curves that we have examined in this chapter have all been drawn as linear.
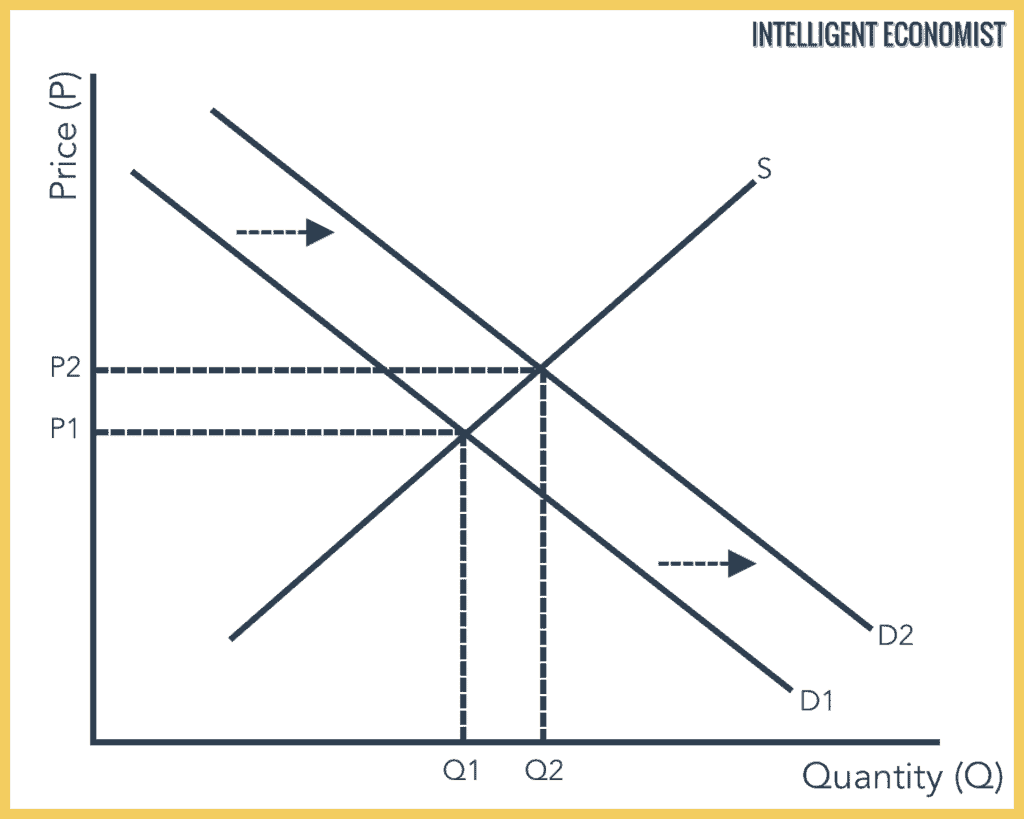
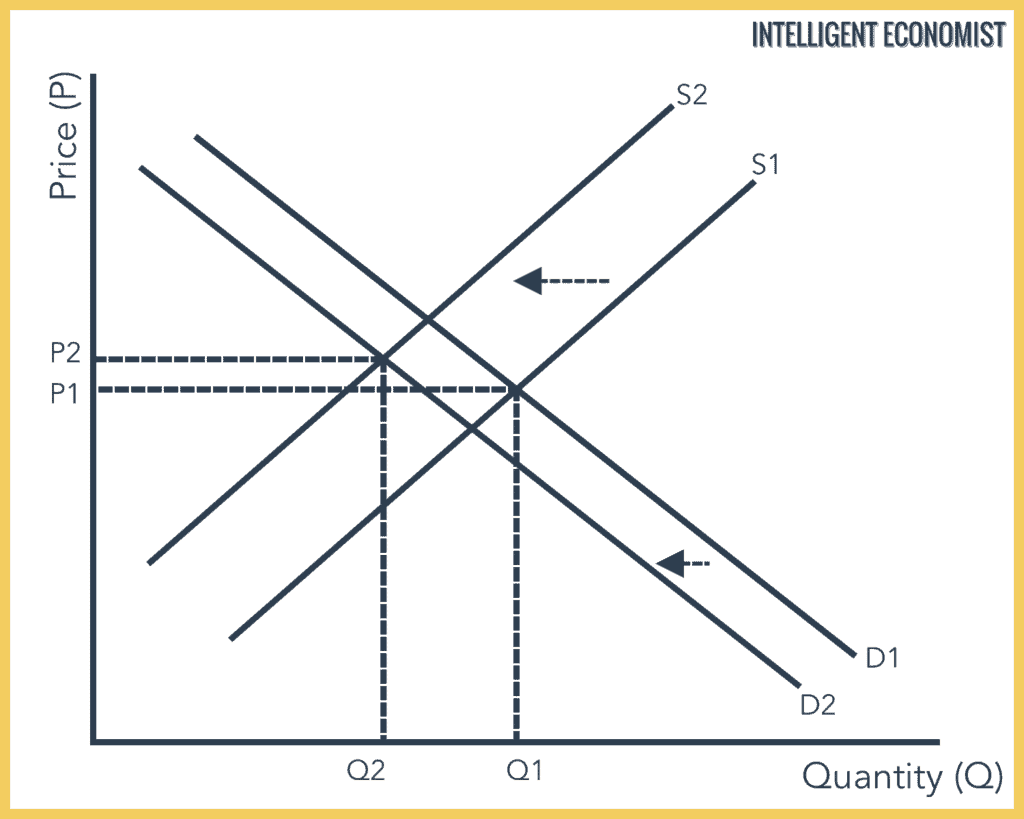
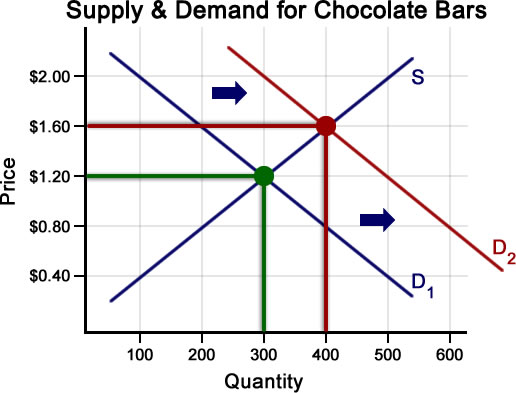
Effectively the equilibrium quantity remains the same however the equilibrium price rises. This has led an increase in quantity q1 to q2 but price has stayed the same. Chart diagram graph description. Supply and demand are one of the most fundamental concepts of economics working as the backbone of a market economy.
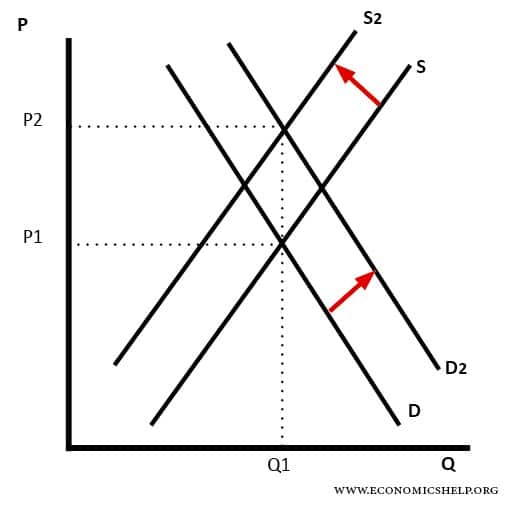
We may now refer to the following four laws of supply and demand. When the increase in demand is equal to the decrease in supply the shifts in both supply and demand curves are proportionately equal. A leftward shifts refers to a decrease in demand or supply. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product that the customers are willing to buy at a certain price and the relationship between price and quantity demanded by.
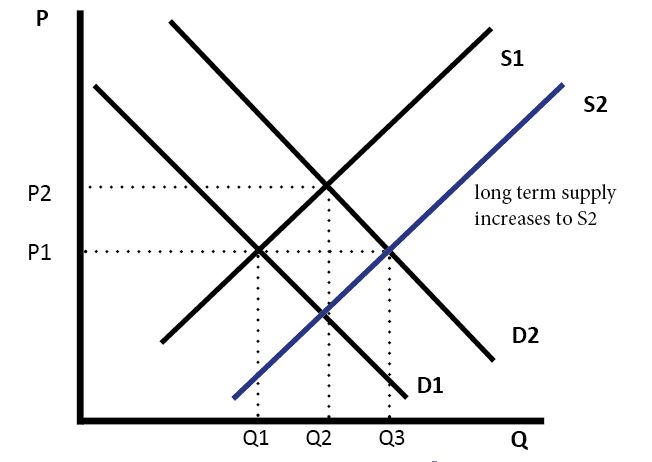
It means that less is demanded or supplied at each price. In addition demand curves are commonly combined with supply curves to determine the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of the market. It is possible that if there is an increase in demand d1 to d2 this encourages firms to produce more and so supply increases as well.